Baling straps, also known as baler straps or banding, play a crucial role in industries like agriculture, recycling, and logistics. These high-tensile straps secure bales of compressed materials such as cardboard, hay, and plastic, ensuring their safe storage and transportation. The growing demand for durable and cost-effective strapping solutions has pushed manufacturers to innovate, leading to the development of advanced production lines that deliver high-quality baling straps at scale. This article takes a closer look at how modern baling strap production lines operate, their technological advancements, and their impact on the industry.

Baling straps are essential for securing compacted materials, which are often transported over long distances and stored in challenging environments. A reliable strap must exhibit high tensile strength, resistance to environmental factors, and ease of application. With industries demanding more efficient and sustainable packaging solutions, manufacturers have invested heavily in modernizing their production processes to meet these needs.
Raw Material Preparation
The production of baling straps begins with sourcing high-quality polyester or polypropylene granules. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and resistance to moisture and UV exposure. The granules are fed into an extruder, where they are melted and prepared for the next stage.
Extrusion and Forming
In the extrusion process, the melted plastic is forced through a specially designed die to form a continuous strip of strap material. The width and thickness of the strap can be adjusted based on customer requirements, with common sizes ranging from 9mm to 19mm.
Stretching and Cooling
To enhance the tensile strength of the straps, the extruded material undergoes a stretching process. This step aligns the molecular structure of the plastic, giving the straps their signature strength and elasticity. The stretched straps are then cooled using water baths or air blowers to solidify their form.
Surface Coating and Finishing
To improve the performance of the baling straps, manufacturers may apply a surface coating, such as a layer of adhesive or a friction-enhancing treatment. This ensures that the straps grip securely around the bales, minimizing the risk of slippage during handling and transportation.
Cutting and Winding
Once the straps are cooled and coated, they are cut to the desired length or wound onto spools for easy storage and transportation. Automated systems ensure precision in cutting and winding, reducing waste and increasing production efficiency.
Quality Control and Testing
Modern production lines incorporate rigorous quality control measures to ensure the straps meet industry standards. Straps are tested for tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to environmental factors. Advanced testing equipment simulates real-world conditions to verify the straps’ performance under stress.
The rise of Industry 4.0 has brought significant advancements to baling strap production lines. Automation, machine learning, and IoT-enabled systems have streamlined production processes, reducing human error and increasing output. Key innovations include:
Automated Monitoring Systems: Sensors and cameras track the production process in real-time, detecting defects and ensuring consistent quality.
Energy-Efficient Machinery: Modern extruders and cooling systems are designed to minimize energy consumption, reducing the environmental impact of production.
Customization Capabilities: Advanced machinery allows for quick adjustments, enabling manufacturers to produce straps in various sizes, colors, and strengths to meet diverse customer needs.
The development of modern production lines has transformed the baling strap industry. Manufacturers can now produce higher-quality straps at a lower cost, making these products more accessible to businesses worldwide. The efficiency of automated systems also allows for faster turnaround times, enabling companies to meet the growing demand for strapping solutions in agriculture, recycling, and logistics.
Moreover, the adoption of sustainable production practices aligns with global efforts to reduce environmental impact. By using recyclable materials and energy-efficient machinery, manufacturers are contributing to a greener, more sustainable future.
High-quality baling straps produced on modern lines offer numerous advantages:
Enhanced Safety: Strong, durable straps ensure that bales remain securely bound, reducing the risk of accidents during handling and transportation.
Cost Savings: Efficient production processes lower the overall cost of straps, offering businesses an economical solution without compromising quality.
Versatility: Baling straps are suitable for various applications, from securing hay bales on farms to bundling compacted plastic in recycling centers.
Sustainability: Many baling straps are made from recyclable materials, helping businesses meet their sustainability goals.
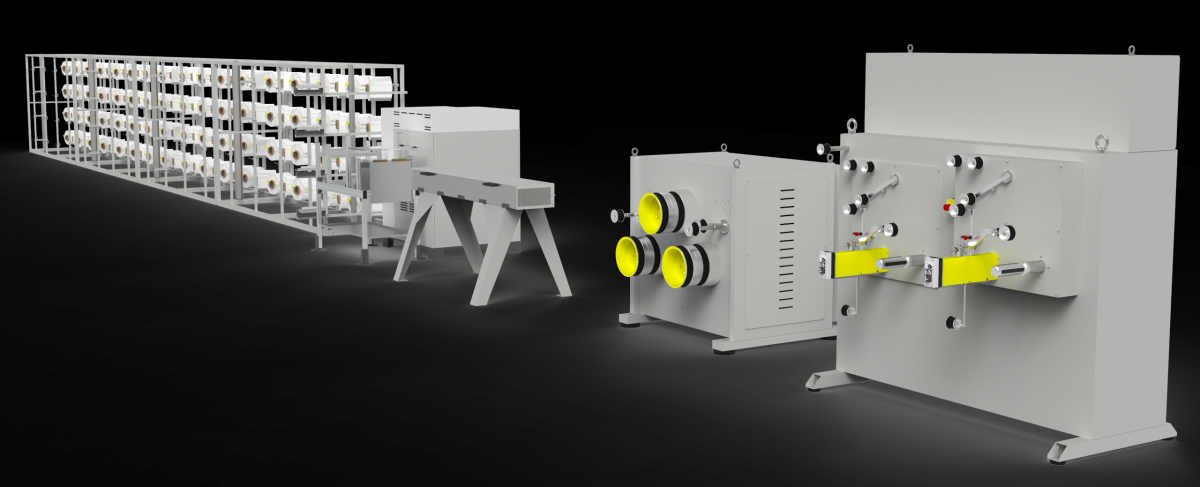
The baling straps production line exemplifies how modern technology and innovative manufacturing practices can revolutionize an industry. By producing stronger, more reliable, and eco-friendly straps, manufacturers are meeting the evolving needs of their customers while driving efficiency and sustainability. As industries continue to rely on baling straps for their packaging and transportation needs, the advancements in production technology will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of this essential product.